The dental implant is one of the most recommended treatments for replacing a missing tooth. Implants, made of three parts namely implant (screw), abutment, and an artificial tooth (prosthesis), give you a fully functional tooth with a strong foundation as the screw is surgically fused in the jawbone for better stability. Dental abutments, made of titanium, zirconia, or gold, act as a connector of implant and artificial tooth.
What Is Dental Implant Abutment?
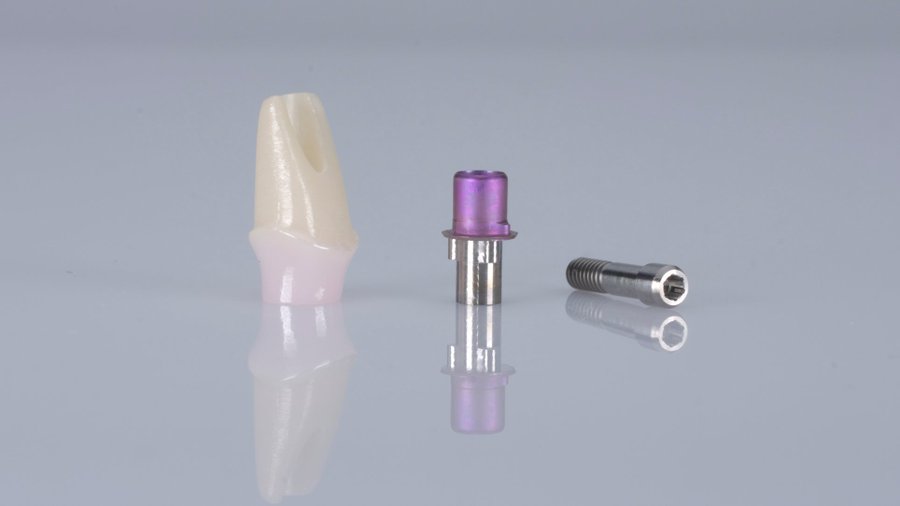
Dental implants are unquestionably the most effective treatment to restore smiles. Following a detailed examination, your dentist will install implants, technically screw made of titanium, in your jawbone. On top of the screw, a metallic connector called an abutment is placed. It connects the implant and the crown—the natural teeth. Although titanium is a more widely used metal in implants, zirconia is getting popular due it better color match with natural teeth. In some cases, healing abutments are also used to facilitate gum tissue generation. These are fitted over implants to create space for the crown.
Types of Dental Implant Abutments
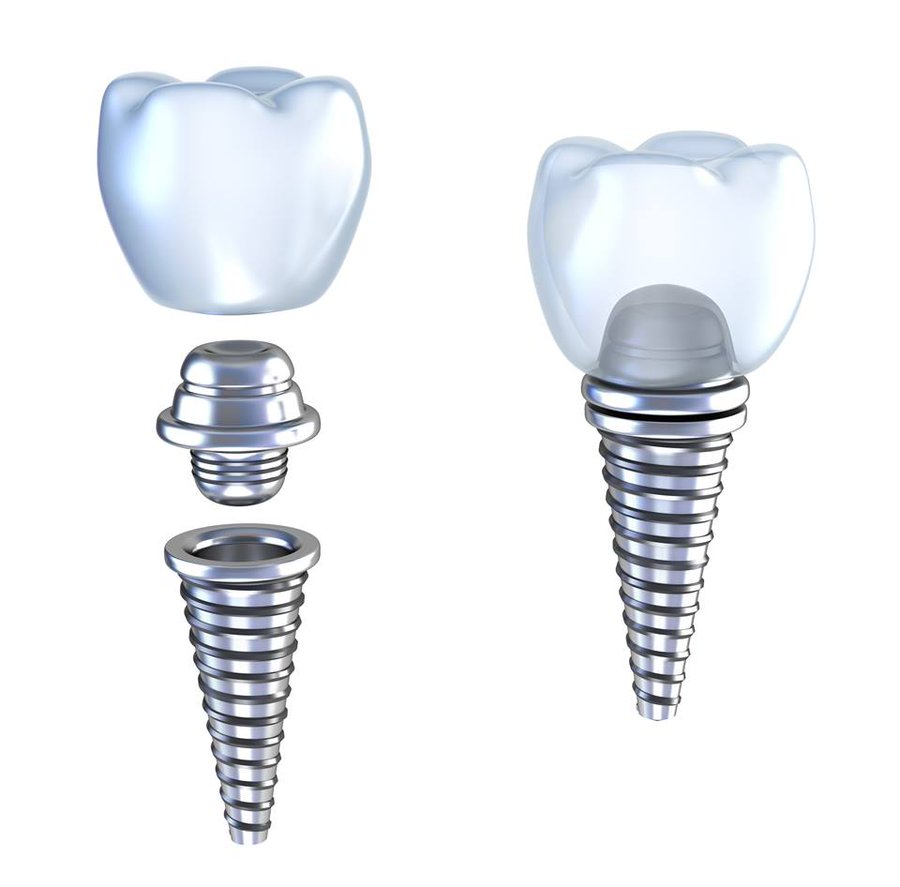
Depending on the treatment plan, whether endosteal and subperiosteal, the type of prosthesis (crown, fixed bridges, or removable dentures), how restoration will be attached to the abutment, and position of the implant inside the mouth cavity, your dentist will use either prefabricated or custom-made abutments.
Prefabricated Abutments
Prefabricated abutments, also called stock abutments, come in different shapes and sizes. Your dentist will choose the best ones based on your dental specification. You have the option of titanium, stainless steel, gold, and zirconia.
Custom-made Abutments
As the name suggests, custom-made abutments are fabricated in labs as per the impression of the top of the implant and gingival. So, you will have a perfectly matching abutment as per your specification.
Whether your dentist is using prefabricated or custom-made abutments, following attachment of abutment to the implant, an impression will be taken to design the restoration.
How is the abutment attached to implant?
Depending on the number of teeth requiring replacement, location of implants within the jaw, bone health, and general health condition, your dentist might recommend additional procedures like sinus augmentation or ridge modification to improve the quality of jawbone.
Your dentist might use gum tissue to cover up abutments so the dental implants could be fused into the jawbone successfully. It normally takes six months to heal. In the next step, the practitioner will cut the gums open, making way to fit crowns.
Alternatively, your dentist might attach a healing abutment, also called the healing cuff, to the external end of the implant. It is used to create enough space for crowns while the gums heal. This eliminates the need for further surgery for crown fitting. Once the implant fuses with the jawbone perfectly, your dentist will remove the healing cuff and fit the crowns.
How the Abutment Works?
The goal of dental implant procedure is to create a strong and durable foundation so that the missing tooth could be restored. So, the first step is to insert the metal post in the jawbone and let it fuse with the bone perfectly, and heal the gums. Once the screws get fused with the jawbone, your dentist will place an abutment, which could be done by making a small incision in the gums.
To avoid second surgery, healing abutment could be temporarily screwed to the implant. Once the gums heal, crowns could be placed after taking an impression. Abutments work like a connector of the implant and the crown. So, it serves as a base for the crown.
Bottom Line
During the healing phase, you have to be a little cautious and eat as per recommendation to avoid chances of infection. The success rate of dental implant treatment is very high, but carelessness could make the treatment painful. In just a few months you will have natural-looking string teeth to smile freely.
